How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, different flight modes, and best practices for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will delve into the essential steps involved in preparing your drone for flight, mastering its controls, and understanding the various flight modes and features available. We will also discuss crucial aspects such as safety protocols, legal regulations, and proper drone maintenance. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to operate a drone safely, efficiently, and legally.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components and verifying system functionality to mitigate potential risks. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and even injury.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Proper training and understanding are crucial for responsible and safe drone operation.
Pre-flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight inspections are paramount for safety and operational success. They identify potential issues before they escalate into problems during flight. Key areas to inspect include battery charge levels (ensuring sufficient power for the intended flight duration), propeller integrity (checking for damage or looseness), and GPS signal strength (confirming a stable connection for accurate positioning and navigation). A weak GPS signal can lead to erratic flight behavior or complete loss of control.
Beginner’s Pre-flight Checklist
- Battery Check: Verify the battery is fully charged and securely connected to the drone.
- Propeller Check: Inspect each propeller for damage, ensuring they are firmly attached and spin freely.
- GPS Signal Strength: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. This usually involves waiting for the indicator on the drone’s controller to display a sufficient number of satellites.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the drone’s body, checking for any damage or loose parts.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) as needed, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Flight Area Assessment: Choose a safe and legal flight area, ensuring clear airspace and avoiding obstacles.
- Emergency Procedures Review: Briefly review emergency landing procedures before takeoff.
Drone Model Pre-flight Procedure Comparison
| Drone Model | Battery Check | Propeller Check | GPS Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Check battery level on controller and app; ensure proper connection. | Visual inspection for damage or looseness; ensure proper installation. | Verify sufficient satellite signal strength on controller and app. |
| Autel EVO II | Check battery level on controller and app; ensure proper connection; check battery health status. | Visual inspection for damage or looseness; check for proper balance. | Verify GPS signal lock on controller screen. |
| Parrot Anafi | Check battery level on controller and app; ensure proper connection. | Visual inspection for damage or looseness. | Verify GPS signal lock and number of satellites acquired. |
| Skydio 2 | Check battery level on controller and app; ensure proper connection. | Visual inspection for damage or looseness. Skydio often self-diagnoses. | System automatically assesses GPS; indication provided on app. |
Pre-flight Safety Flowchart
The flowchart begins with a “Start” node. It then branches to “Battery Check,” visually represented by a battery icon. Next is “Propeller Check,” depicted with a propeller symbol. “GPS Check” follows, shown as a satellite icon. A “Visual Inspection” step is next, represented by a drone image with a magnifying glass.
Finally, “Calibration” is shown with a compass and level icon. All steps lead to a “Safe to Fly?” decision node. If yes, the process proceeds to “Takeoff.” If no, it returns to the failed check for correction. The flowchart concludes with an “End” node.
Taking Off and Landing

Safe and controlled takeoff and landing are fundamental aspects of drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and damage. Understanding different techniques for various environments is also essential for successful and responsible flying.
Safe Takeoff Procedure, How to operate a drone
A safe takeoff involves gradually increasing throttle to lift the drone vertically. Maintain smooth and controlled movements, avoiding sudden inputs. Adjust altitude as needed to maintain a safe clearance from the ground and any obstacles. Always monitor the drone’s position and orientation.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques in Different Environments
Open fields provide ample space for straightforward takeoffs and landings. Confined spaces require more precise control and careful obstacle avoidance. Wind conditions significantly impact takeoff and landing, requiring adjustments to compensate for drift. Near water bodies, additional caution is needed in case of unexpected malfunctions.
Automated vs. Manual Takeoff and Landing
Automated features offer convenience and simplicity, especially for beginners. However, manual control provides greater precision and adaptability in challenging conditions. Understanding the limitations of both approaches is vital for safe operation.
Emergency Landing Procedures
- Assess the Situation: Quickly determine the cause of the emergency and assess the surrounding environment.
- Reduce Throttle: Gently lower the throttle to initiate descent.
- Choose a Landing Spot: Identify a safe and clear area for landing, avoiding obstacles and people.
- Execute Landing: Execute a controlled descent and landing, maintaining stability.
- Post-Landing Check: After landing, inspect the drone for any damage.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls is crucial for safe and effective operation. Smooth and precise maneuvers require practice and a grasp of the control inputs. Avoiding common mistakes ensures safe flight and prevents accidents.
Drone Control Stick Functions
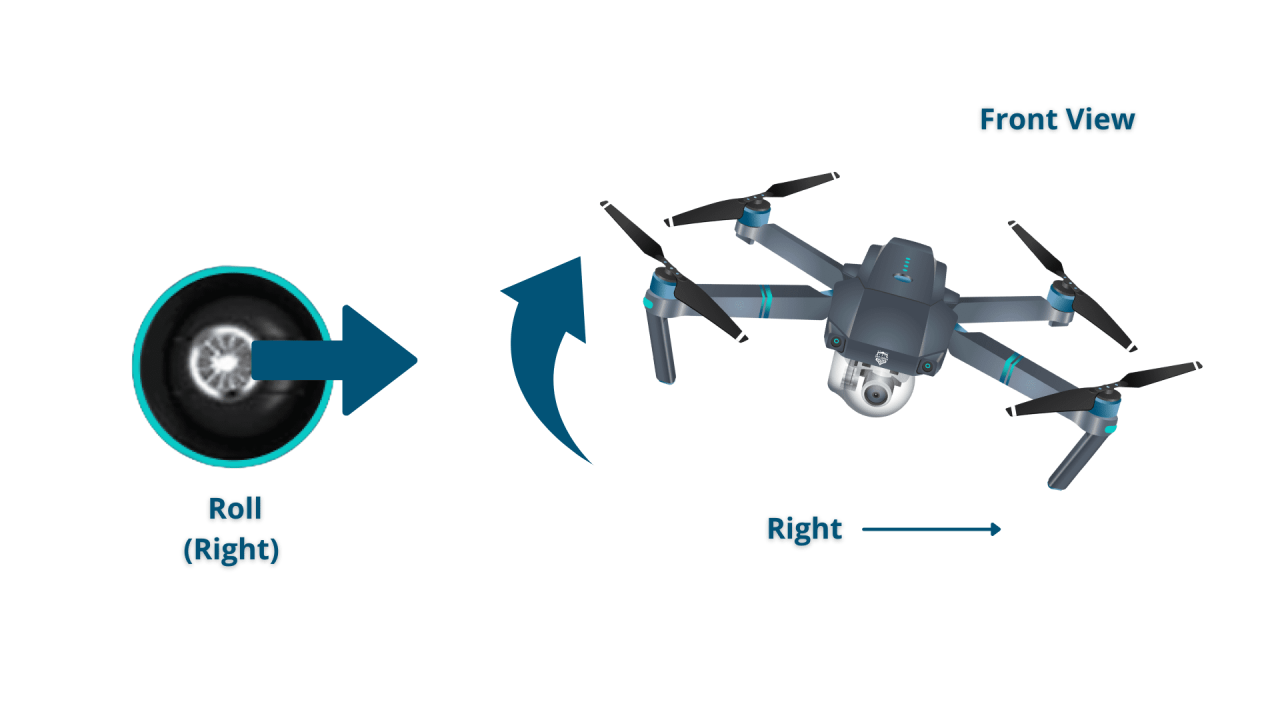
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. The left joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls roll (tilting left and right) and pitch (tilting forward and backward). Some drones use alternative input methods such as touchscreens or gesture control.
Smooth and Precise Maneuvering
Smooth movements are achieved by using gentle inputs on the control sticks. Avoid jerky movements and sudden changes in direction. Practice flying in open areas to develop control and coordination.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Stable flight is maintained through precise control inputs and by adjusting the drone’s attitude (orientation) in response to wind or other disturbances. Keeping an eye on the drone’s position and orientation is key.
Common Beginner Mistakes
- Over-correction: Overreacting to unexpected movements can lead to instability and loss of control.
- Ignoring Wind Conditions: Failing to account for wind can result in unexpected drift and difficulties maintaining position.
- Insufficient Battery: Flying with insufficient battery charge can lead to unexpected power loss and crashes.
- Neglecting Safety Procedures: Skipping pre-flight checks or ignoring safety guidelines can lead to accidents.
Flight Modes and Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes and features that enhance both ease of use and capabilities. Understanding these modes and features is crucial for safe and effective operation, enabling users to tailor the drone’s behavior to different situations and skill levels.
Flight Mode Explanations
Beginner mode limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, making it easier to control. Sport mode increases speed and responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots. GPS mode utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability. Other modes may include cinematic mode for smooth, slow movements and follow-me mode for automated tracking.
Flight Mode Benefits and Limitations
| Flight Mode | Description | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness. | Easy to control for beginners; reduces risk of accidents. | Limited maneuverability and speed. |
| Sport Mode | Increases speed and responsiveness. | Enhanced maneuverability and speed for experienced pilots. | Increased risk of accidents for inexperienced pilots. |
| GPS Mode | Uses GPS for precise positioning and stability. | Improved stability and precision; easier to maintain position. | Can be less responsive in areas with weak GPS signal. |
Drone Feature Analysis
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle Avoidance | Automatically avoids obstacles. | Increased safety and ease of use; reduces risk of collisions. | May not detect all obstacles; can be unreliable in complex environments. |
| Follow-Me Mode | Automatically follows a designated subject. | Convenient for filming; frees up the pilot’s attention. | Requires a clear line of sight; can be affected by obstructions. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Automatically returns to the home point. | Increased safety; ensures the drone returns even if signal is lost. | Accuracy depends on GPS signal strength; may not be reliable in all conditions. |
Photography and Videography with a Drone: How To Operate A Drone

Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is crucial for producing high-quality content. Achieving stable footage and smooth transitions enhances the visual appeal.
High-Quality Aerial Capture
High-quality aerial photography and videography require understanding camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering these settings and achieving the desired results. Using appropriate filters can also enhance image quality.
Compelling Shot Composition
Effective composition involves framing the subject effectively within the shot. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images. Varying camera angles and perspectives adds dynamism and interest.
Achieving Stable Footage
Stable footage is essential for professional-looking videos. Using a gimbal (a stabilizing mechanism) significantly reduces camera shake and motion blur. Flying smoothly and avoiding sudden movements also contributes to stable footage. Post-processing techniques can further enhance stability.
Visual Guide: Camera Angles
The visual guide would show various camera angles, such as high-angle shots (looking down on the subject), low-angle shots (looking up at the subject), and eye-level shots (on par with the subject). Each angle would be illustrated with a visual representation showing its perspective and the effect on the final image or video. For example, a high-angle shot would demonstrate a sense of scale and overview, while a low-angle shot would emphasize the subject’s size and dominance.
Drone Maintenance and Battery Care
Regular maintenance and proper battery care are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation. Neglecting these aspects can lead to premature wear and tear, malfunctions, and even accidents.
Post-Flight Cleaning and Maintenance
After each flight, clean the drone’s body and propellers, removing any dirt, debris, or moisture. Inspect for any signs of damage and address any issues promptly. Store the drone in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as pre-flight checks and maneuvering, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of flight operation, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and master the art of aerial navigation. Safe and responsible drone operation is key to enjoyable and successful flights.
Proper Battery Care
Proper battery care involves charging the batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions, avoiding overcharging or deep discharging. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
Common Maintenance Issues and Troubleshooting
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- Battery Issues: Check battery health and replace if necessary.
- Gimbal Problems: Calibrate or repair the gimbal if experiencing issues.
- Software Glitches: Update the drone’s firmware to address software issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A sample maintenance schedule might include a daily visual inspection, a weekly thorough cleaning, and a monthly more in-depth inspection of all components, including the battery and motor.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires adherence to local laws and regulations. Understanding these rules and obtaining necessary permits ensures safe and legal drone operation, avoiding potential fines or legal issues.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Laws and regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules in your area regarding drone registration, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations. These regulations often cover aspects such as maximum altitude, flight distances from airports, and restrictions in populated areas.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. These permits may be required for commercial use, flights in restricted airspace, or specific types of drone operations.
Flight Restrictions
Drones are typically restricted from flying near airports, sensitive areas (such as power plants or military bases), and densely populated areas. Always check for airspace restrictions before each flight, using online resources or apps that provide real-time airspace information.
Responsible and Ethical Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation includes respecting privacy, avoiding disturbing wildlife, and being mindful of other airspace users. Flying safely and legally is paramount for maintaining a positive image of drone technology and ensuring its continued acceptance.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill, careful planning, and responsible decision-making. From meticulous pre-flight checks to understanding the nuances of flight controls and adhering to legal regulations, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding flying experience. By consistently applying the techniques and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently navigate the skies, capture breathtaking aerial footage, and contribute to the responsible growth of the drone community.
Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations.
FAQ Compilation
What is the ideal wind speed for flying a drone?
Generally, wind speeds below 15 mph are considered safe for most drones. Higher wind speeds can make controlling the drone difficult and increase the risk of accidents.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during a flight?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available) and attempt to return the drone to a safe landing area manually. Many drones have a “return-to-home” feature, but manual control is often necessary in emergencies.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s good practice to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve been transporting it or if you’re flying in an area with strong magnetic interference.
